Endometriosis
Comprehensive Guide to Managing Endometriosis Through Nutrition and Treatment
Introduction
Endometriosis is a chronic gynaecological condition characterized by the growth of endometrial-like tissue outside the uterus. This tissue responds to hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle, leading to inflammation, pain, and potential fertility issues. While there is no cure for endometriosis, a multifaceted approach involving dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and targeted treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Need to consult?
Quickly Book an Appointment.
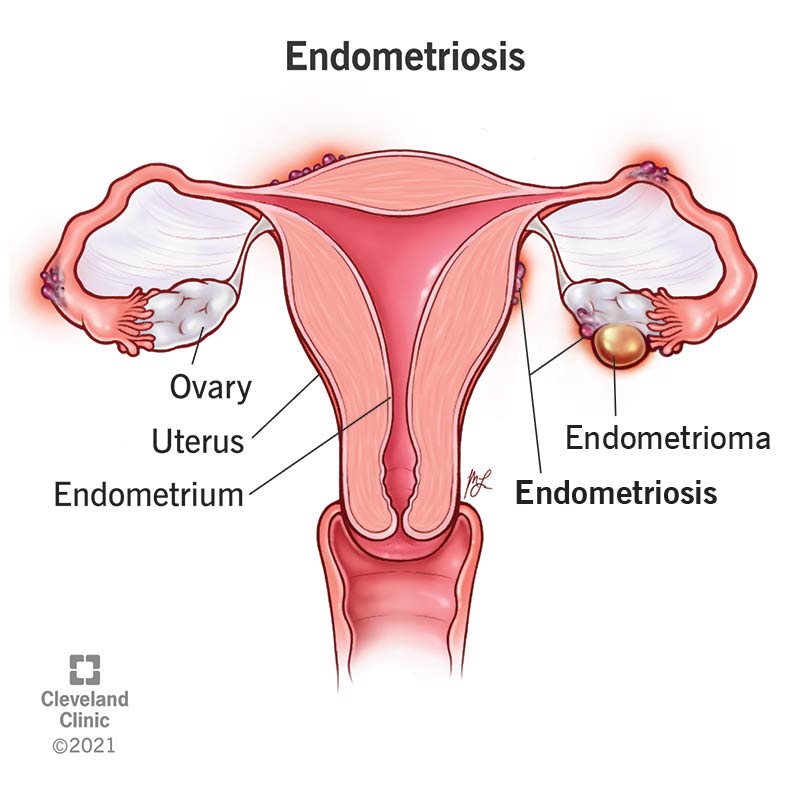
Causes of Endometriosis
The exact cause of endometriosis remains unclear, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- Retrograde menstruation: Backflow of menstrual blood through the fallopian tubes into the pelvic cavity.
- Hormonal imbalances: Abnormal levels of estrogen and progesterone may promote the growth of endometrial tissue.
- Immune system dysfunction: Impaired immune response may fail to recognize and eliminate misplaced endometrial cells.
- Genetics: A family history of endometriosis may increase the risk of developing the condition.
Symptoms of Endometriosis
Endometriosis can manifest with various symptoms, which may include:
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Painful menstrual periods (dysmenorrhea)
- Pain during intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia)
- Infertility or difficulty conceiving
- Gastrointestinal symptoms (bloating, constipation, diarrhea)
- Fatigue and mood changes
Diagnosis of Endometriosis
Diagnosing endometriosis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI. However, the gold standard for diagnosis is laparoscopic surgery with tissue biopsy to visualize and confirm the presence of endometrial implants.
Dietary and Lifestyle Modifications
Nutritional Approach to Endometriosis Management:
Research suggests that dietary modifications can play a role in managing endometriosis symptoms and reducing inflammation. Key dietary recommendations include:
- Emphasizing a plant-based diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
- Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids from fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
- Limiting the consumption of red meat and high-fat dairy products.
- Including anti-inflammatory herbs and spices in cooking, such as turmeric and ginger.
Lifestyle Modifications for Endometriosis:
In addition to dietary changes, lifestyle modifications can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being. Strategies may include:
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as yoga, walking, or swimming.
- Practising stress management techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises.
- Ensuring adequate sleep and prioritizing relaxation.
- Avoiding exposure to environmental toxins, such as endocrine-disrupting chemicals found in certain plastics and pesticides.
Treatment Approaches
Medical Management of Endometriosis:
Treatment options for endometriosis aim to relieve symptoms and reduce disease progression. They may include:
- Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Hormonal therapies, including birth control pills, hormonal IUDs, or GnRH agonists, to suppress menstruation and reduce endometrial growth.
- Surgical interventions, such as laparoscopic excision of endometrial implants or hysterectomy in severe cases.
Comprehensive Care and Support:
At Foodnwellness, our dedicated team of healthcare professionals provides personalized support and guidance for managing endometriosis. We offer comprehensive care tailored to individual needs, including:
- Nutritional counselling to optimize diet and address specific dietary concerns.
- Lifestyle coaching to promote stress management, exercise, and sleep hygiene.
- Coordination with medical providers to ensure integrated treatment approaches.
Ongoing support and education to empower individuals in managing their condition effectively.
Conclusion
Endometriosis can present significant challenges, but with the right approach, it is possible to effectively manage symptoms and improve quality of life. By adopting a balanced and nutritious diet, making lifestyle adjustments, and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals with endometriosis can take proactive steps towards better health and well-being.
If you or a loved one are struggling with endometriosis, we encourage you to reach out to the experienced team at Foodnwellness for compassionate care and comprehensive support. Together, let’s navigate this journey towards wellness.
Barnard, N.D. et al. (2021). Nutrition in the prevention and treatment of endometriosis: A review. Journal of Gynecology Obstetrics and Human Reproduction.
Let's get started with treating your condition...
At Food & Wellness we believe that every individual is different and needs special attention. We adapt our programme to your existing lifestyle and try not to change anything drastically so you can easily transition. Over a period of time we ensure results and help you restore your health.
Related Articles
Salt and Water Retention: Why Your Weight Jumps Overnight and What to Do
If you woke up heavier than yesterday, you are not alone and you are not “failing”. Salt and Water Retention: Why Your Weight Jumps Overnight (and What to Do) is one of the most common weight-loss frustrations, and it can feel confusing because the scale changes so fast. Salt and Water Retention: Why Your Weight Jumps Overnight (and What to Do) comes down to one simple truth: most overnight jumps are water weight, not fat.

The Hidden Link Between Insulin Resistance, Fatty Liver, and Cholesterol
The hidden link between insulin resistance, fatty liver, and cholesterol is something many people live with for years without realising it. Blood sugar may look “slightly high,” cholesterol numbers may be borderline, and an ultrasound may quietly mention fatty liver. These problems often appear separate, but in reality, they are deeply connected.

Longevity and Hormone Supportive Eating: Nourishing the Body for Healthy Aging
Longevity is not just about living longer it’s about aging with vitality, balance, and resilience. Hormone-supportive eating plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, reducing inflammation, and preserving long-term health as the body ages.
