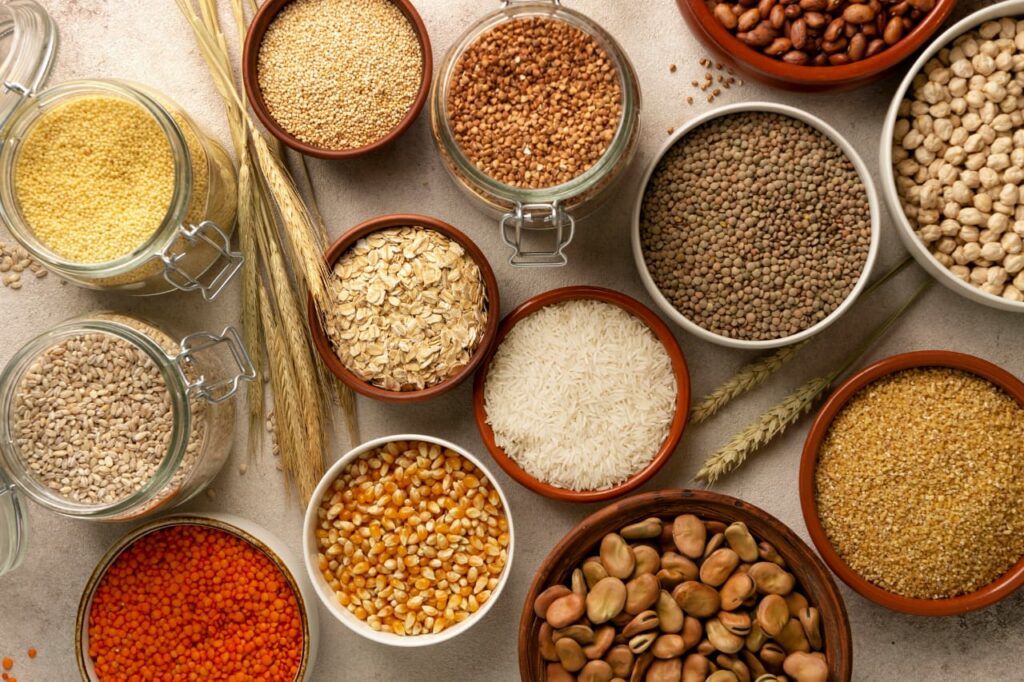
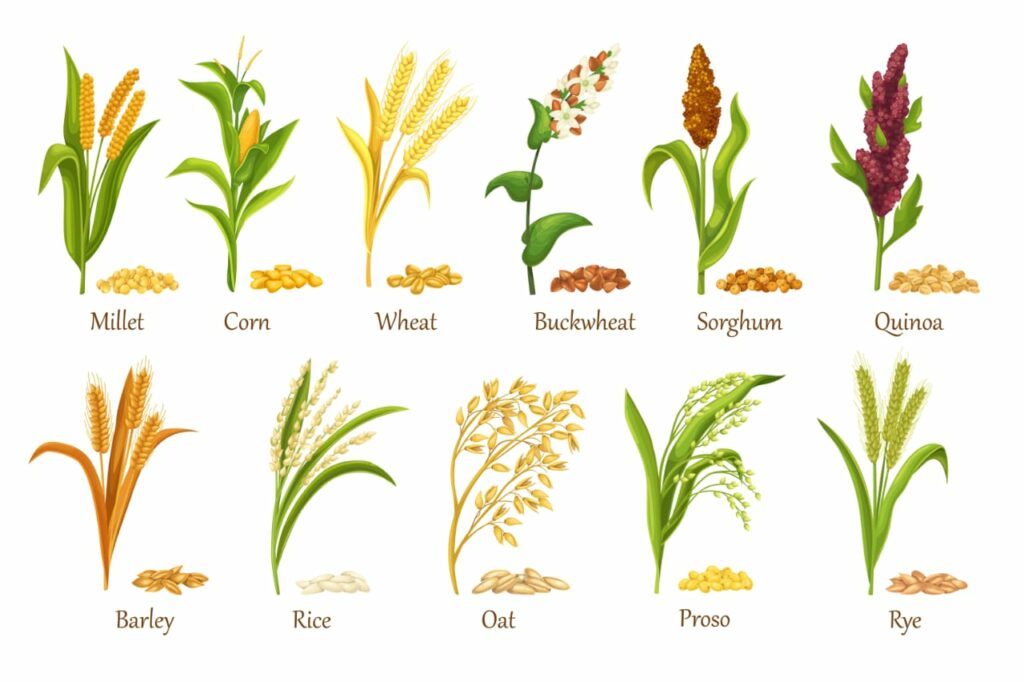
Ancient grains, such as quinoa, farro, spelt, amaranth, and Indian varieties like millets, sorghum, and finger millet, have been cultivated for thousands of years and are now celebrated for their rich nutritional profiles and potential health benefits. Incorporating these grains into modern diets can provide a variety of essential nutrients, enhance digestive health, and support overall well-being. This blog delves into the health benefits of ancient grains and how they can be a valuable addition to your diet.
Ancient Grains: Nutrient-Dense Powerhouses
They boast impressive nutrient content. Unlike refined grains that lose many nutrients during processing, people typically consume ancient grains in their whole form, retaining their nutrient-rich bran and germ. Here are some key nutrients found in various ancient grains:
Quinoa: This gluten-free grain is a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids. It is also rich in fiber, iron, magnesium, and manganese.
Farro: A type of wheat, farro is high in protein, fiber, magnesium, and zinc. It also contains B vitamins, which are essential for energy metabolism.
Spelt: Another type of wheat, spelt is rich in protein, fiber, iron, magnesium, and zinc. It is also a good source of B vitamins and antioxidants.
Amaranth: This grain is high in protein and fiber and is a good source of magnesium, phosphorus, and iron. It also contains vitamin C, which is rare for grains.
Millets: Popular in India, millets like pearl millet (bajra), foxtail millet (kangni), and little millet (kutki) are rich in fiber, protein, and essential minerals like magnesium, phosphorus, and iron.
Sorghum (Jowar): This gluten-free grain is high in protein, fiber, antioxidants, and essential nutrients such as magnesium, iron, and B vitamins.
Finger Millet (Ragi): Known for its high calcium content, ragi is also rich in fiber, protein, and essential amino acids. It contains significant amounts of iron and antioxidants.

Ancient Grains Benefits for Digestive Health
The high fiber content in ancient grains plays a crucial role in promoting digestive health. Fiber adds bulk to the stool, which helps to maintain regular bowel movements and prevent constipation. Additionally, fiber can support a healthy gut microbiome by providing food for beneficial bacteria. A diverse and balanced gut microbiome is linked to improved digestion, better immune function, and even mental health benefits.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Ancient grains have a lower glycemic index compared to refined grains, meaning they cause a slower and more gradual rise in blood sugar levels. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those trying to manage their blood sugar levels. The fiber content in ancient grains also helps to slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, further aiding in blood sugar control.
Heart Health
Including ancient grains in your diet can support heart health in several ways. The fiber in these grains can help to lower cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol in the digestive system and preventing its absorption. Additionally, many ancient grains are rich in antioxidants, which help to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which are risk factors for heart disease. Magnesium, found in grains like quinoa, farro, and sorghum, is also essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
Weight Management
The high fiber and protein content in ancient grains can help with weight management by promoting feelings of fullness and reducing overall calorie intake. Protein is known to increase satiety and reduce appetite, while fiber slows digestion and prolongs the feeling of fullness. Incorporating ancient grains into meals can help to control hunger and support healthy weight loss or maintenance.

Incorporating Ancient Grains into Your Diet
Adding them to your diet is simple and versatile. Here are some easy ways to incorporate them into your meals:
Breakfast: Use quinoa or amaranth in place of oats for a nutrient-packed porridge. Add fresh fruits, nuts, and seeds for extra flavor and nutrition. In India, try ragi porridge or a millet-based upma.
Salads: Toss cooked farro or spelt with your favorite vegetables, herbs, and a light dressing for a hearty and nutritious salad. In Indian cuisine, you can prepare a millet salad with fresh vegetables and a lemon dressing.

Main Dishes: Substitute ancient grains for rice or pasta in your favorite recipes. Quinoa pairs well with a variety of proteins and vegetables. For an Indian twist, make jowar roti or a millet-based khichdi.
Baking: Use spelt flour or amaranth flour in your baking recipes for a healthier twist on traditional baked goods. You can also try millet flour in Indian flatbreads like bhakri.
Conclusion
Ancient grains offer a myriad of health benefits, from improved digestion and heart health to better blood sugar management and weight control. Their nutrient density, sustainability, and versatility make them an excellent addition to any diet. By incorporating these grains into your meals, you can enjoy their rich flavors and reap the numerous health benefits they provide.
Incorporate ancient grains into your diet today and experience the difference they can make in your overall health and well-being. Whether you’re looking to improve your digestive health, manage your weight, or simply enjoy more nutrient-dense foods, ancient grains are a delicious and nutritious choice.


